Static & Dyanmic Allocation of Memory
Static & Dyanmic Allocation of Memory
Static memory allocation allots memory from the stack. Dynamic memory allocation allots memory from the heap. Once the memory is allotted, it will remain from the beginning to end of the program. Here, the memory can be alloted at any time in the program.
Memory Space by OS
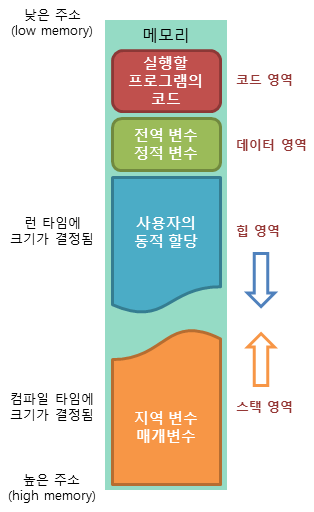
- Code : code
- Data : Global variables, static variables
Allocated when the program is started and deallocated when the program is finished. - Heap : Dynamic memory allocation
Allocated by ** - Stack : local variables, parameters, return address Allocated when function is called and deallocated when the function is finished.
Why use dynamic memory allocation?
-
Memory efficiency: Since RAM memory resources are limited, dynamic memory allocation is used to allocate memory from the heap. This is done to avoid the stack overflow error. Stack overflow prevents using other memory other than its onwn stack memory. When You can allocate memory dynamically when you need and free it when you don’t need it.
-
Unknow size of the array: Ram Dynamic memory allocation is used when the size of the memory is not known at the time of allocation. We can avoid waste of memory by using dynamic memory allocation. However, when we forget to free the memory, it will cause memory leak.
The code pair below should come together
malloc-> free
new -> delete -
In case of normal variables and functions, they are allocated from the stack. However, when you
int a = 10;